The Voyager spacecraft, launched in the late 1970s, represents humanity's quest to explore the cosmos beyond our solar system. As we stand on Earth, it is fascinating to consider how far these probes have traveled and the wealth of information they have gathered. With Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 now journeying through the vastness of interstellar space, their current locations serve as a testament to human ingenuity and curiosity. In this article, we will delve into the current status of these remarkable spacecraft, their missions, and what we can learn from their ongoing travels.
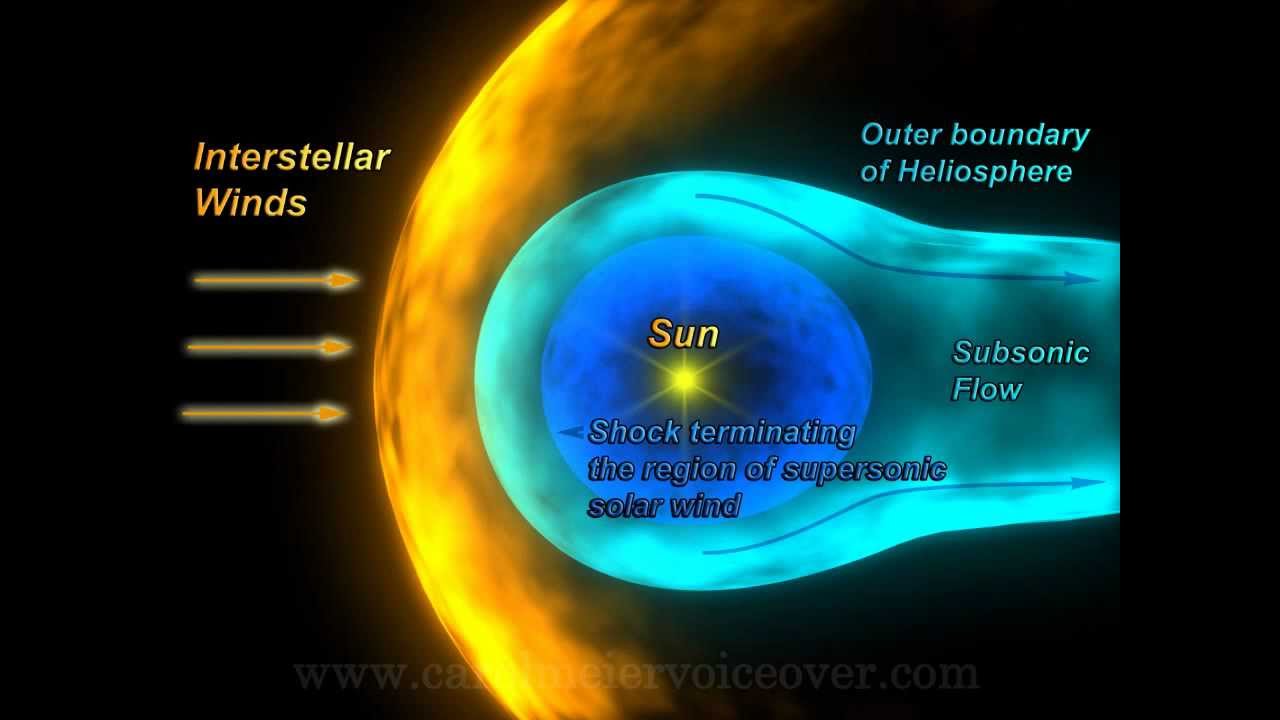
As we explore the Voyager's current location, we reflect on the groundbreaking discoveries made during their missions. Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 have provided invaluable data about the outer planets, their moons, and the heliosphere—the bubble-like region of space dominated by the solar wind. The information gathered by these spacecraft has expanded our understanding of the solar system and beyond, inspiring future generations of scientists and explorers.
With the Voyager probes now in interstellar space, their current locations are not just coordinates on a map; they symbolize humanity's aspirations to reach further into the unknown. In this article, we will examine the latest updates on the Voyager's current location, the incredible technology that keeps them operational, and the future of interstellar exploration.
What is the Current Location of Voyager 1?
Voyager 1, launched on September 5, 1977, is the farthest human-made object from Earth. As of now, Voyager 1 is over 14 billion miles away from our planet, traveling at a speed of approximately 38,000 miles per hour. Its current location is in the interstellar medium, where it continues to send back data to NASA. The probe crossed the heliopause in 2012, marking its entry into interstellar space, and it remains operational, sending valuable information about cosmic rays and magnetic fields.
How Does NASA Track Voyager's Current Location?
Nasa utilizes a combination of ground-based antennas and advanced tracking technology to monitor the Voyager spacecraft. The Deep Space Network (DSN), consisting of large radio antennas located in California, Spain, and Australia, plays a crucial role in maintaining communication with Voyager 1 and Voyager 2. By analyzing the signals sent back from the spacecraft, scientists can calculate their distance and trajectory with remarkable precision.
What Kind of Data is Voyager 1 Sending Back?
Despite being billions of miles away, Voyager 1 continues to provide groundbreaking data, including:
- Measurements of cosmic rays that help scientists understand the radiation environment beyond the solar system.
- Information about the interstellar magnetic field, aiding in our understanding of how the solar wind interacts with the surrounding space.
- Studies of the heliosphere's boundary, providing insights into the solar system's size and shape.
What is the Current Location of Voyager 2?
Launched on August 20, 1977, Voyager 2 is currently also in interstellar space, trailing slightly behind Voyager 1. As of now, its distance from Earth is over 12 billion miles. Voyager 2 is unique as it is the only spacecraft to have visited Uranus and Neptune, providing us with invaluable data about these distant planets. Its current location signifies a journey through both the outer planets and into the vastness of the interstellar medium.
How Does Voyager 2 Communicate with Earth?
Similar to Voyager 1, communication with Voyager 2 is maintained through NASA's Deep Space Network. The signals sent from Voyager 2 take over 18 hours to reach Earth, meaning that any data received is significantly delayed. Scientists meticulously analyze this data to continue learning about the interstellar environment and the characteristics of the heliosphere.
What Discoveries Has Voyager 2 Made in Interstellar Space?
Voyager 2 is also sending back valuable data, including:
- Measurements of solar wind particles in the interstellar medium.
- Insights into the composition of the interstellar medium and cosmic rays.
- Data on the magnetic field surrounding the spacecraft, enhancing our understanding of the universe.
What Challenges Do Voyager Probes Face in Interstellar Space?
As Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 navigate through interstellar space, they face numerous challenges, including:
- Decreasing power levels: Both spacecraft rely on radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs) for power, which are gradually losing their energy output.
- Communication delays: As the distance increases, the time it takes for signals to travel to and from the probes becomes more significant.
- Cosmic radiation: The probes are exposed to high levels of radiation in interstellar space, which can affect their instruments and systems.
What is the Future of the Voyager Missions?
The future of the Voyager missions is uncertain, as the spacecraft are operating beyond their intended lifespan. However, scientists remain optimistic about the data they continue to send back. The current location of Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 offers a unique opportunity to study the interstellar medium and gain insights into the behavior of cosmic phenomena. NASA plans to keep the probes operational as long as possible, with the hope of receiving valuable information well into the next decade.
What Can We Learn from the Voyager's Current Location?
The ongoing journeys of Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 provide us with profound insights into the universe. Their current locations challenge our understanding of the solar system's boundaries and the interstellar medium. As humanity continues to explore the cosmos, the data collected by these probes will serve as a foundation for future missions, inspiring generations to reach for the stars.
In conclusion, the Voyager probes represent a monumental achievement in space exploration. The current locations of Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 remind us of our potential to explore the unknown and the importance of scientific inquiry. As we continue to monitor their journeys, we are not only learning about distant regions of space but also reflecting on our place in the cosmos.
Discover The Power Of Home Depot Steam Cleaners For A Spotless Home
Exploring The Culinary Delights Of Eating Giant Clam
Unveiling The Olympic Ceremony: The Assassin's Creed Connection